PAD can be controlled or even prevented by lifestyle changes, such as exercising and diet, weight reduction, control of Diabetes and measures to lower blood cholesterol. The single most important step one can take to slow PAD is to stop smoking.
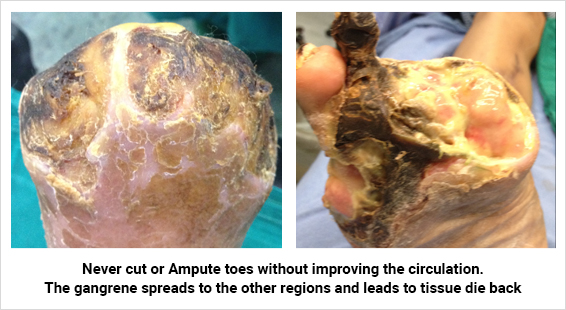
PAD is a disease of the blood vessels that affects 15% of the population worldwide. In PAD, the arteries that carry blood to the arms or legs become narrowed or clogged, leading to slowing or stoppage of blood flow. The disease most commonly affects the legs and sometimes occurs in the arms. Many people do not give much importance to initial symptoms - such as pain or numbness in the legs or arms - because they mistakenly believe it is a normal part of aging. Ignoring the symptoms may lead to gangrene of the limbs and eventually limb loss.
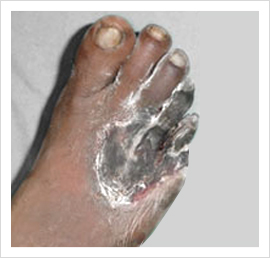
It is usually caused by atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries. Atherosclerosis is a gradual process in which cholesterol and scar tissue build up inside the artery. This over a period of time blocks the artery, thereby depriving the limb of its blood supply.
A blood clot from the heart can get pushed into the limb arteries leading to sudden stoppage of blood supply to the limb. This causes severe pain and discoloration of the limb. This is an emergency situation, meriting prompt action to save the limb.
The most common symptom of PAD is leg pain on walking, also called as claudication, which goes away after a few minutes of rest. (Intermittent claudication). Claudication distance is important in deciding invasive treatment options.
Other symptoms
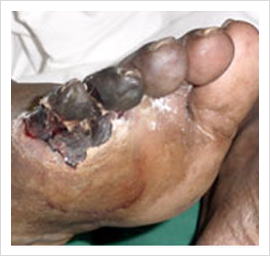
Anyone can develop PAD, but it occurs most often in people who are over 50 years. Men are more likely to be affected than women. Factors that contribute to the disease include smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, a family history of heart or vascular disease, and obesity.
PAD can be controlled or even prevented by lifestyle changes, such as exercising and diet, weight reduction, control of Diabetes and measures to lower blood cholesterol. The single most important step one can take to slow PAD is to stop smoking.
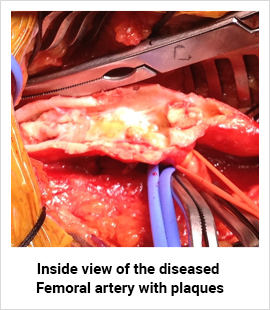
The ideal treatment for PAD depends on a number of factors, including your overall health, the location of affected artery, and the size and nature of the blockage or narrowing in the artery etc. If the blockage has been sudden, prompt treatment within 6 hours is a must to avoid loss of limb.
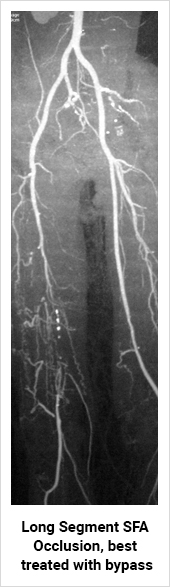
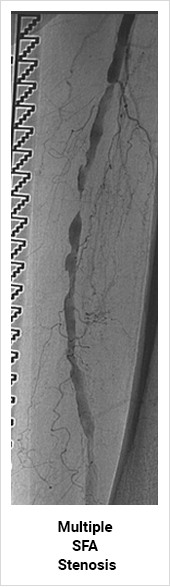
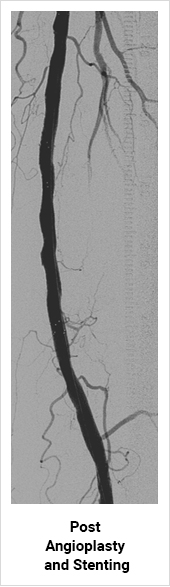
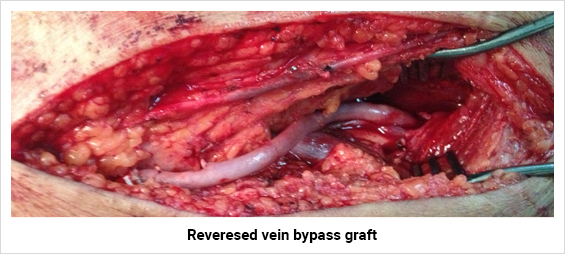
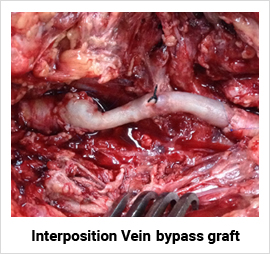
For arteries that have been blocked chronically, treatment options vary depending on the site and the length of blockage. For short segment blockage, angioplasty and stenting is a good treatment option. For long segment blockage a bypass surgery is the best option. Nowadays with the advent of Drug Elluting Balloon (DEB) and Stents DES), the results of angioplasty and stenting have improved.
Dr. Pankaj Patel a vascular surgeon has expertise in peripheral vascular diseases, varicose veins and deep vein thrombosis